Benefits of GST (List of Indirect Taxes): Check Complete of Indirect Taxes Included and Excluded in GST. Introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) will indeed be an important perfection and the next logical step towards a widespread indirect tax reforms in India. GST Scheme was supposed to be implemented from 1st July 2017 but this deadline seems difficult to be met as the Constitutional Amendment Bill has been stuck in Rajya Sabha. However, the department has said that the GST can be implemented anytime in 2017 once the Bill is passed. GST implementation will lead to immense scope, opportunities and challenges for the chartered accountant professionals having expert knowledge in the subject. This article seeks to provide a quick and sound understanding of List of Taxes Included in GST and Benefits of GST Advent of GST is bringing drastic changes in the indirect tax structure. Although GST is propagated as single indirect tax, it will be major indirect tax and other indirect tax will remain intact. Professional need to understand which taxes are getting subsumed and which taxes will remain post GST.
List of Taxes Included in GST and Benefits of GST
Taxes which will get added:
Central Tax – earliest GST Model Law specified as CGSTState Tax- earliest GST Model Law specified as SGSTIntegrated Tax- earliest GST Model Law specified as IGSTUnion Territory Tax- earliest GST Model Law specified as UTGSTGST Compensation Cess
Indirect Taxes That Will Be Included Under GST
Following taxes will be subsumed in Goods & Services Tax as mentioned above :
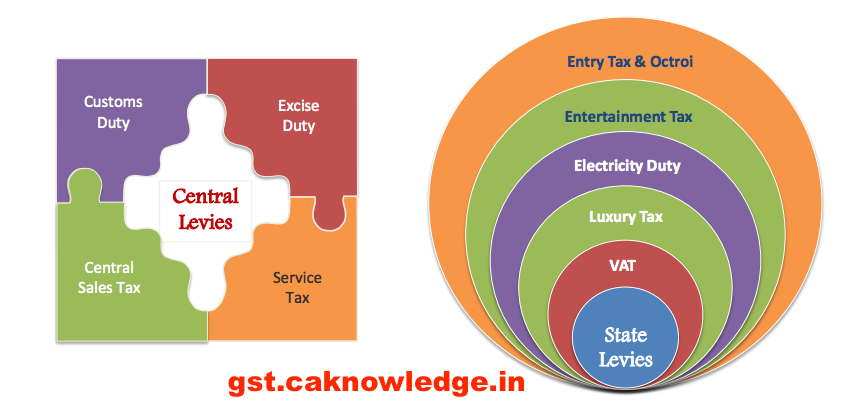
State taxes which will be subsumed in SGST
VAT/Sales taxEntertainment tax (unless it is levied by local bodies)Luxury taxTaxes on lottery, betting and gamblingState cess and surcharges to the extent related to supply of goods and services.Entry tax not on in lieu of octroiElectricity Duty
Central taxes which will be subsumed in CGST:
Central Excise : Central Excise Act, 1944 except as respects goods included in entry 84 (Alcohol for human consumption)of the Union List of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution and Central Excise on Petroleum ProductsServices Tax under Finance Act, 1994Central Sales Tax – CST Value Added Tax – VAT Additional duty of customs -CVD Additional duty of customs equal to the, excise duty leviable on like goods produced or manufactured in India. This is levied under Section 3 of Customs Tariff Act, 1975 Special Additional duty – SAD Imported goods are also liable to a Special additional duty at a rate specified in Section 3A of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975.Education Cess under Finance Act – ECHigher Secondary education Cess under Finance Act – SHEC Swachha Bharat Cess – SBCKrishi Kalyan Cess – KKC Cess collected by Central Govt under various heads like Automobile Cess, Tractor Cess, Textile CessetcMedicinal ExciseEntry Tax on Goods Under Entry of Goods into Local Areas ActEntry Tax on Motor Vehicles Under Entry Tax of Motor Vehicles into Local Areas ActPurchase TaxTaxes on Lottery Betting gambling Under Betting Tax Act of respective StateLuxury Tax Under Luxuries Act of respective StatesEntertainment Tax Under Entertainment tax Act of respective StatesState Cess / surchagesLBT – Local Body TaxOctroiTax on sale of Forest Produce by Government or Forest Development Corporation.
List of Taxes Not Included in GST
Taxes That May or May Not Be Subsumed Due To No Consensus Between The Central And The State Governments and various other reasons
Basic Customs Duty – BCDSurcharge on Customs duty Surcharge at the rate of 10% of the Basic Customs Duty is levied on imported goods under Section 90 of the Finance Act, 2000 (unless exempted by a notification). Customs Cess – Safeguard duty under Section 8B of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 Anti-dumping duty under Section 9A, Customs Tariff Act 1975State ExciseStamp DutyProperty Tax levied by Local BodiesCentral Excise as respects goods included in entry 84 (Alcohol for human consumption) of the Union List of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution Central Excise on Petroleum Products – GST applicability date on petroleum products will be notified subsequentlyVAT on Petroleum Products – GST applicability date on petroleum products (i.e. petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas and aviation turbine fuel) will be notified subsequentlyProfession Tax License fee on entry of vehicles under THE CANTONMENTS ACT, 2006Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
Benefits of GST
GST has been envisaged as a more efficient tax system, neutral in its application and attractive in distribution. The advantages of GST are:
Wider tax base, necessary for lowering the tax rates and eliminating classification disputesElimination of multiplicity of taxes and their cascading effectsRationalization of tax structure and simplification of compliance proceduresHarmonization of center and State tax administrations, which would reduce duplication and compliance costsAutomation of compliance procedures to reduce errors and increase efficiency
Reduces transaction costs and unnecessary wastages: A single registration and a single compliance will suffice for both SGST and CGST provided government produces effective IT infrastructure and integration of states level with the union. Eliminates the multiplicity of taxation: The reduction in the number of taxation applicable in a chain of transaction will help to reduce the paper work and clean up the current mess that is brought by existing indirect taxation laws. One point single tax: There would be focus on business rather than worrying about their taxation that may crop at later stages. This will help the business community to decide their supply chain, pricing modalities and in the long run helps the consumers being goods competitive as price will no longer be the function of tax components but function of sheer business intelligence and innovation. Reduces average tax burdens: The cost of tax that consumers have to bear will be certain and it is expected that GST would reduce the average tax burdens on the consumers. Reduces the corruption: As the number of taxes reduces so does the number of visits to multiple departments reduces and hence, the reduction in corruption. In all cases except a few products and States, there would be uniformity of tax rates across the States. Recommended Articles
Karnataka GST ActGST Registration ProcedureState GST ActGST DownloadsReturns Under GSTGST RegistrationGST RatesGST FormsHSN Code ListGST LoginGST Registration last dateGST Due DatesGST Rules